 自我指导的学习模型的四个阶段
自我指导的学习模型的四个阶段
经过教学人员
自我指导的学习不是新的 - 但也许被误解了。
在上面的链接帖子中,特里·希克(Terry Heick)想知道自我指导的学习与教育目的之间的关系:
The goal of the model isn’t content knowledge (though it should produce that), but rather something closer to wisdom–learning how to learn, understanding what’s worth understanding, and perhaps most importantly, analyzing the purpose of learning (e.g., personal and social change). It also encourages the student to examine the relationship between study and work–an authentic ‘need to know’ with important abstractions like citizenship and legacy.
多年来,在成人教育和职业方面进行了研究,出于多种原因,自我指导的学习在受欢迎程度上正在增加,包括对公立教育的不满,以及在线提供丰富的正式和非正式学习材料。毕竟这是“信息时代”。
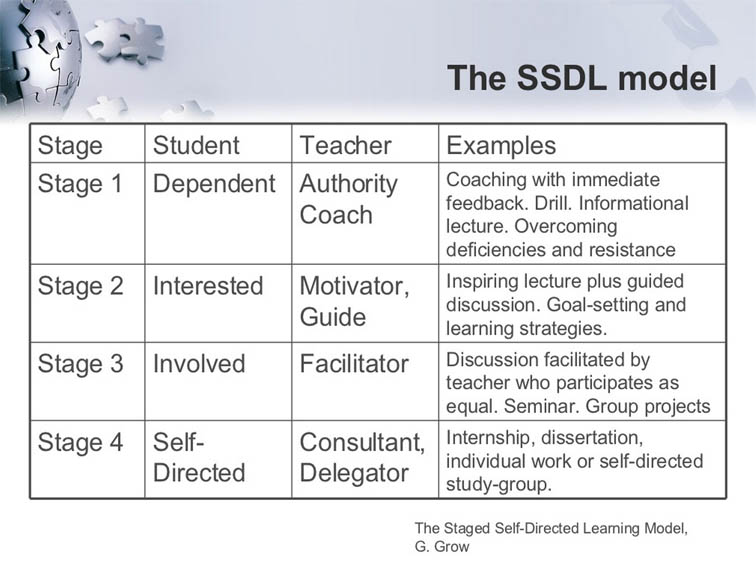
自我指导的学习是一种响应,基于Gerald Grow的模型,Slideshare用户Barbara Stokes在此图表中捕获了捕获。这四个阶段 - 与逐步释放责任模型- 在下面出现。
自定向学习模型的四个阶段
学习者老师
阶段1依赖的权威,教练
示例:立即反馈的指导。钻头。信息讲座。克服缺陷和抵抗力。
阶段2:有兴趣的动机,指南
示例:鼓舞人心的演讲以及指导性讨论。目标设定和学习策略。
阶段3:参与主持人
示例:由教师以平等参与的教师的讨论。研讨会。小组项目。
阶段4:自我指导的顾问,代表们
示例:实习,论文,个人工作或自我指导的研究小组。
教学理论:上演的自我指导的学习模型G.Grow。从芭芭拉·斯托克斯(Barbara Stokes);自我指导的学习模型的四个阶段


